Image Search Techniques rule the internet now. Think about your own habits for a second—do you read long blocks of text first, or do your eyes go straight to photos, thumbnails, reels, and screenshots? From Instagram and Pinterest to news sites and online stores, visuals are the fastest way we communicate, learn, and decide.
Because of that, knowing how to search with images and for images has gone from a nice bonus to a basic digital survival skill.
That’s exactly what image search techniques are about.
Instead of relying only on plain text, today’s tools let you search using:
-
Keywords
-
Uploaded photos
-
Colors and patterns
-
Faces, objects, and even logos
In this guide, you’ll learn what image search really is, how it works under the hood, the different techniques you can use, the best tools available, and where all of this is heading. By the end, you’ll not only understand the theory—you’ll know how to apply it in your daily and professional life.
What Is Image Search?
At its core, Image Search Techniques is a way to find pictures that match a certain idea, object, person, or visual style. Instead of only typing in text like “red shoes” or “Eiffel Tower at night,” you can also:
-
Upload a photo
-
Paste an image URL
-
Select a part of an existing image
Then, the search engine looks for:
-
Exact matches
-
Similar visuals
-
Related context and pages
So what can you actually do with that?
-
Find the original creator of a photo
-
Identify a product you spotted in a random post
-
Check whether an image has been edited or misused
-
Discover related visuals for your design, research, or campaign
This is why image search is huge in fields like:
-
Journalism and fact-checking
-
Digital marketing and branding
-
eCommerce and product discovery
-
Photography, design, and creative work
Image Search Techniques used to be simple: type a keyword, get a grid of pictures. Now, thanks to AI and machine learning, it can understand content, composition, and even context. That means you get smarter, more relevant results—not just more of the same.
How Does Image Search Actually Work?
Let’s demystify the tech for a minute—without going full textbook.
When you use Image Search Techniques, two main approaches are at play:
-
Keyword-based (traditional)
-
Visual-based (AI-driven)
Here’s the basic flow.
1. Breaking an image into “digital pieces”
When you upload an image, the system doesn’t see “a nice handbag” or “a cute cat.” It sees:
-
Colors
-
Shapes and silhouettes
-
Edges and outlines
-
Textures (smooth, rough, patterned)
-
Spatial layout (where things are in the frame)
These details are turned into a kind of visual fingerprint—a numeric representation that describes what’s in the image.
2. Matching against a massive database
That fingerprint is then compared against billions of images stored and indexed across the web. The algorithms look for:
-
Similar shapes and compositions
-
Patterns that match
-
Objects and scenes that resemble what’s in the query image
At the same time, if it’s a keyword search, the engine also uses:
-
Image titles
-
Alt text
-
Captions
-
Text around the image on the page
So for text searches, it leans more on metadata. For visual searches, it leans more on pixels and patterns.
3. Returning ranked results
Image Search Techniques engine will then show you images and pages that are:
-
Exact matches
-
Visually close
-
Contextually relevant
For example:
-
If you upload a red handbag, the system reads its shape, size, color, and style, then shows:
-
The same product from other stores
-
Similar bags in the same style or color
-
-
If you upload a landmark photo, it detects architecture, skyline, or special structures and maps it to a location—then surfaces travel guides, articles, and more.
Behind all of this, deep learning and computer vision models continually improve as they see more data. The result? Faster, more accurate, more “human-like” image understanding.
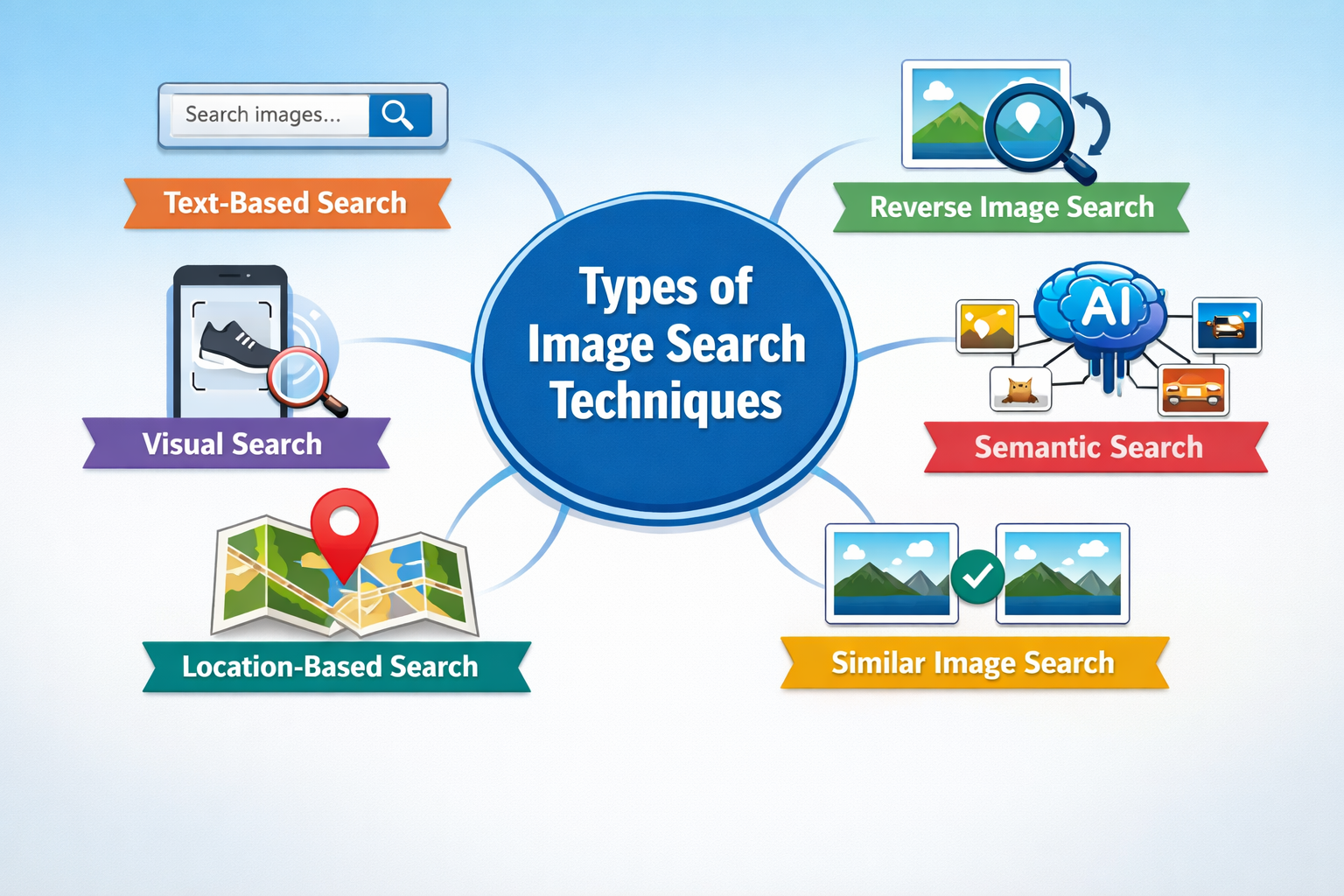
Types of Image Search Techniques
Not every Image Search Techniques works the same way. Different goals call for different techniques. Knowing which method to use is half the battle.
Let’s break down the main types.
1. Keyword-Based Image Search
This is the classic method most people know.
You type words into a search bar, like:
-
“sunset over mountains”
-
“business meeting illustration”
-
“healthy breakfast flat lay”
The search engine then retrieves images whose metadata matches your query:
-
File names
-
Titles
-
Alt text
-
Captions
-
Nearby on-page text
Best for:
-
General images (nature, objects, concepts)
-
Stock-like visuals for blogs, ads, or presentations
-
When you already know how to describe what you want
The key here is specificity. “Shoes” is too broad. “Black leather running shoes for men” gives far better results.
2. Reverse Image Search
Reverse image search flips the usual process.
Instead of starting with text, you start with an image:
-
Upload a photo, screenshot, or design
-
Paste the URL of an image online
The search engine then tries to find where that image (or similar ones) appears on the internet.
What it’s great for:
-
Spotting plagiarism or stolen content
-
Tracing the original source of a picture
-
Checking whether a viral image is real or recycled
-
Finding higher-resolution or uncropped versions
If you suspect a photo has been misused or copied, reverse image search shows you:
-
Other sites using it
-
Different edits, crops, or manipulations
-
Earlier appearances that reveal the original context
It’s a powerful tool for authenticity and copyright checks.
3. Visual Similarity Search
Visual similarity search doesn’t only look for exact matches. Instead, it looks for images that look like your input.
It focuses on:
-
Style
-
Layout
-
Colors
-
Patterns
Imagine you love a specific sofa, jacket, or poster design. Visual similarity search can:
-
Show alternatives with similar patterns or shapes
-
Match styles across different brands
-
Help you “shop the look” instead of hunting by brand or model name
This is huge in:
-
Fashion
-
Interior design
-
Lifestyle and decor
-
eCommerce discovery
Think of it as a digital mood board generator: you show it one idea, it shows you a whole world of related visuals.
4. Color and Pattern-Based Search
Sometimes, the main thing that matters in an image isn’t the object—it’s the color palette or pattern.
Color and pattern-based search lets you:
-
Filter images by specific colors
-
Look for visuals that match a brand palette
-
Find patterns like stripes, florals, geometric shapes
Designers, advertisers, and brand managers use this to:
-
Keep campaigns visually consistent
-
Maintain brand identity across visuals
-
Quickly spot on-brand visuals in large libraries
Many image platforms allow you to:
-
Select a color swatch
-
Apply color filters
-
Search by gradient or tone
When visual coherence matters, this technique is a game-changer.
5. Object and Facial Recognition Search
This is where things get very smart—and a bit sci‑fi.
Object recognition can detect:
-
Cars, animals, products, tools
-
Food, furniture, and household items
-
Logos and branded elements
Facial recognition can detect:
-
Similar faces
-
Repeated appearances of the same person
-
Public profiles or pages where a face appears
These techniques are used by:
-
Law enforcement (identification, investigations)
-
Media organizations (verifying photos, naming people)
-
Social platforms (tag suggestions, content moderation)
Examples:
-
Facial recognition can check if the same person appears across multiple photos.
-
Object detection can identify a specific model of car or type of pet in an image.
They make searches more precise, but they also raise important privacy and ethics questions—something the industry is still grappling with.
When Should You Use Each Image Search Technique?
Using the right method for the right task makes your life much easier.
-
Keyword-based search
Use when you:-
Need general visuals or concepts
-
Are brainstorming ideas
-
Know exactly how to describe what you want
-
-
Reverse image search
Use when you:-
Want to find the source of an image
-
Need to check authenticity or plagiarism
-
Are looking for better quality or original versions
-
-
Visual similarity search
Use when you:-
Care about style and aesthetics
-
Want design inspiration or similar products
-
Are matching decor, outfits, or moodboard images
-
-
Color/pattern-based search
Use when you:-
Need to stick to a brand palette
-
Want visuals with specific tones or patterns
-
Are building cohesive campaigns or designs
-
-
Object/facial recognition search
Use when you:-
Need to identify people, products, or items
-
Are doing media analysis or investigations
-
Need granular recognition beyond simple labels
-
Often, the best approach is to combine methods. For example:
-
A marketer might:
-
Start with a keyword search for “summer travel campaign”
-
Pick a favorite image
-
Run a reverse image search to check usage rights
-
Use visual similarity search to find related creatives
-
Knowing the strengths of each technique helps you get better results faster.
Top 7 Tools for Powerful Image Search

There are dozens of tools out there, but a few stand out for their features and reliability. Here are some of the best.
1. Google Images – The Standard for Keyword and Reverse Search
Google Images is still the default choice for most people.
What you can do:
-
Type keywords for traditional image search
-
Click the camera icon to:
-
Upload an image
-
Paste an image URL
-
Google then:
-
Finds visually similar images
-
Shows sites using that picture
-
Sometimes suggests a “best guess” description
Why people love it:
-
Massive index of web images
-
Fast and generally accurate
-
Works well for:
-
General research
-
Content creation
-
Quick authenticity checks
-
For everyday use, Google Images is hard to beat.
2. Lenso.ai – Best for Face Search and AI-Powered Reverse Search
Lenso.ai is built specifically for AI-powered reverse image search, with strong facial recognition capabilities.
What it offers:
-
Upload an image and explore categories like:
-
People
-
Duplicates (great for copyright checks)
-
Places
-
Related
-
Similar
-
-
Detects:
-
Exact duplicates
-
Stolen or reused content
-
Potential catfish or fraud
-
Key features:
-
Advanced filters by keywords and domains
-
Sorting by newest/oldest or best/worst match
-
Alert system:
-
No result yet? Create a free alert.
-
Get notified when new matches appear later.
-
Perfect for:
-
Creators protecting their work
-
Individuals monitoring where their photos appear
-
Anyone worried about identity misuse or scams
3. TinEye – Best for Tracking Image Origins and Duplicates
TinEye is a dedicated reverse image search engine.
Its strengths:
-
Excellent at tracking where an image first appeared
-
Finds:
-
Resized
-
Cropped
-
Slightly edited versions
-
Widely used by:
-
Journalists
-
Photographers
-
Brands and agencies
Why it’s valuable:
-
Helps detect copyright violations
-
Shows image “family trees”—how a visual evolved across the web
-
Very reliable for duplication and misuse detection
If you care about authenticity and ownership, TinEye is a must‑have.
4. Bing Visual Search – Great for Shopping and Object Identification
Bing Visual Search turns image searching into an interactive experience.
What makes it special:
-
You can draw a box around part of an image (e.g., just a lamp or a pair of shoes)
-
It then finds:
-
Similar products
-
Related items
-
Matching visuals
-
Best for:
-
Online shoppers looking for:
-
Look‑alike products
-
Cheaper alternatives
-
Hard‑to‑describe items
-
-
People identifying objects, places, or styles
Plus, its integration with Microsoft Edge makes visual search only a right‑click away.
5. Pinterest Lens – Ideal for Lifestyle, Fashion, and Décor Ideas
Pinterest Lens brings visual search into the lifestyle and inspiration space.
How it works:
-
Take a photo or upload one
-
Pinterest scans it and shows:
-
Similar styles
-
Related ideas
-
Themed boards
-
Perfect for:
-
Home décor inspiration
-
Outfit ideas and fashion styling
-
Recipes, DIY, crafts, and event planning
For creators and lifestyle enthusiasts, Pinterest Lens turns everyday objects into creative prompts.
6. Yandex Images – Strong in Reverse Image Recognition
Yandex Images is part of Russia’s major search engine but used worldwide by researchers and OSINT communities.
Why it stands out:
-
Very strong face and object recognition
-
Often surfaces results that:
-
Google and Bing miss
-
Come from different regions or local platforms
-
Useful for:
-
Cross-checking reverse image search results
-
Investigations and deep research
-
Finding obscure sources for photos, artworks, or memes
If you’re doing serious verification or global tracking, Yandex is a valuable alternative.
7. Shutterstock – Perfect for Copyright Protection and Image Tracking
Shutterstock is known primarily as a stock photo platform—but it also offers a powerful reverse search feature to registered users.
What it helps with:
-
Checking whether your licensed images are being reused incorrectly
-
Finding similar stock photos in its library
-
Protecting intellectual property
Ideal for:
-
Photographers
-
Agencies
-
Brands with licensed visual assets
It turns stock management into a more controlled, safer process.
Best Practices for Effective Image Searching
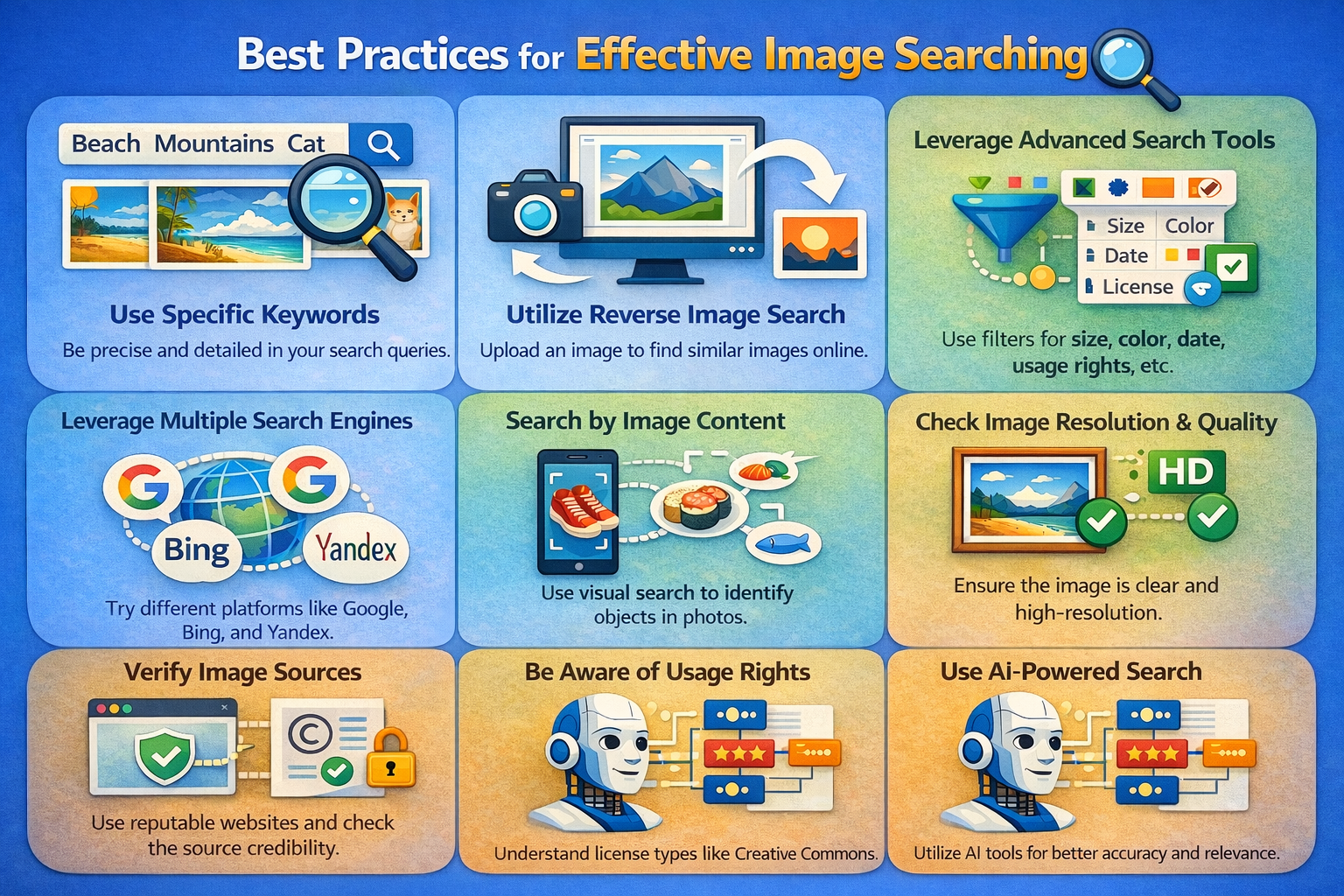
You can have the best tools in the world and still get bad results if you use them poorly. A few simple habits can dramatically improve your searches.
1. Use clear, high-quality images
For uploads:
-
Avoid blurred, pixelated, or over‑cropped images
-
Try to keep the main subject visible and uncluttered
The cleaner the image, the easier it is for algorithms to detect patterns.
2. Be specific with keywords
For text-based searches:
-
Use descriptive phrases:
-
Instead of “shoes,” try “black leather men’s running shoes”
-
Instead of “dog,” try “golden retriever puppy playing in garden”
-
-
Add context: “vector,” “illustration,” “logo,” “transparent background”
Specificity cuts through noise and improves relevance.
3. Combine tools for better coverage
Don’t rely on just one platform. Try:
-
Google Images for general coverage
-
TinEye for origin and duplicates
-
Lenso.ai or Yandex for face or deep recognition
-
Pinterest Lens for lifestyle inspiration
Each has different strengths and databases.
4. Use filters to narrow results
Most platforms let you filter by:
-
Size
-
Color
-
Type (photo, illustration, icon)
-
Usage rights
-
Date
Use these filters to:
-
Avoid copyright issues
-
Find fresh or older content
-
Get visuals that actually fit your purpose
5. Respect copyright and usage right
This one is non‑negotiable.
-
Always check whether you’re allowed to use an image
-
Look for:
-
Creative Commons licences
-
Stock licenses
-
Commercial vs. editorial restrictions
-
Ethical image use doesn’t just protect you legally—it also supports the creators behind those visuals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Image Search
Even experienced users slip up. Avoid these traps:
-
Using low-quality or heavily edited image
Over‑cropped, filtered, or distorted images confuse recognition algorithms. -
Relying on a single search engine
No platform has the entire web. Cross‑checking improves accuracy. -
Ignoring filters and advanced option
Skipping filters often means wading through pages of irrelevant images. -
Not checking licensing before use
Grabbing a random image from “Google Images” doesn’t mean it’s free to use. -
Overcomplicating keyword query
Stuffing in too many unrelated terms can break relevance. Keep it focused and clear.
The goal is simple: clean input, smart tools, ethical output.
Practical Applications of Image Search
Image search isn’t just for curiosity. It’s embedded in serious work across industries.
1. Journalism and Media Verification
Journalists and fact‑checkers use image search to:
-
Verify if a news photo is genuine
-
Detect if an image is old but being pass off as new
-
Identify manipulated or misleading visuals
Before publishing, many editors now run reverse image checks as standard practice.
2. eCommerce and Online Shopping
Retailers and marketplaces use visual search to:
-
Let customers upload a photo to find similar products
-
Recommend related items based on style
-
Reduce friction when users cannot describe a product in words
This leads to:
-
Higher engagement
-
Better user experience
-
Increased conversion rates
3. Design and Creative Work
Designers, photographers, and marketers rely on image search to:
-
Gather inspiration and references
-
Explore color and style trends
-
Ensure visual consistency across campaigns
Color and pattern-based searches are especially useful for brand work.
4. Education and Research
Teachers, students, and researchers use image search to:
-
Find visual aids and illustrations
-
Verify the origin of historical or scientific images
-
Avoid plagiarism in assignments and presentations
It supports both better learning and better academic integrity.
5. Law Enforcement and Security
Authorities use object and facial recognition to:
-
Identify suspects from camera footage
-
Track stolen goods or counterfeit products
-
Cross‑reference images across multiple sources
While powerful, this use case also comes with major privacy and ethical responsibilities.
6. Marketing and Brand Protection
Brands use image search to:
-
Monitor how their logos and imagery are used online
-
Detect unauthorized use of brand visuals
-
Measure how far campaigns travel across regions and platforms
It’s a key part of modern brand monitoring and reputation management.
7. Social Media Monitoring and Creator Protection
Influencers and content creators use these tools to:
-
Track reposts of their photos and videos
-
Find uncredited uses of their work
-
Discover new audiences and unexpected reach
For people whose business depends on visuals, image search is both a shield and a spotlight.
The Future of Image Search
So where is all this going?
Image recognition is nowhere near its ceiling. As AI improves, we can expect:
1. Deeper visual understanding
Future systems won’t just see “two people at a table.” They’ll interpret:
-
Emotions
-
Interactions
-
Relationships between objects
That means richer, more contextual results like:
-
“happy family dinner in rustic kitchen”
-
“stressed office worker late at night”
2. Seamless AR and real-time search
With augmented reality and wearables:
-
You’ll point your camera at an object and instantly get:
-
Product info
-
Reviews
-
Prices
-
Recipes (for food)
-
Travel info (for landmarks)
-
Imagine snapping a meal and getting calorie counts and recipes on the spot.
3. Personalization and intent-aware search
Machine learning will better understand:
-
Your style preferences
-
Past searches
-
Typical use cases
This will allow image search to adapt results to your intent rather than just your keyword.
4. Stronger focus on privacy and ethics
As image search gets more powerful, questions around:
-
Facial recognition
-
Data storage
-
Consent
will only get louder. Expect tighter rules, clearer settings, and more transparency.
In short, image search is evolving from a simple tool into a visual assistant that understands not just what you see, but what you mean.
Conclusion
Image search techniques have quietly transformed how we interact with visual content online.
From a simple keyword query, we now have:
-
Reverse image search
-
Visual similarity search
-
Color and pattern filters
-
Object and facial recognition
These tools help you:
-
Identify products and places
-
Verify authenticity and fight misinformation
-
Protect copyright and brand identity
-
Fuel creativity and inspiration
Whether you’re a student, marketer, journalist, designer, or just a curious user, understanding how these Image Search Techniques work—and when to use each one—gives you a real edge in a visual-first internet.
Image search isn’t just a technical concept. It’s a practical skill that helps you move through the online world with more confidence, more creativity, and more control.
Use it to find what inspires you, verify what you’re shown, and protect what you create. The more visual the web becomes, the more powerful this skill will be.




